There are only a few times in one’s life where you’ll need to purchase windows. Many people flippantly make this decision without any research. Bad idea. I wanted to provide you with the Top 10 most important criteria to consider when selecting windows for your home. It is extremely important to make sure that you consider energy efficiency when choosing your windows.
If you neglect any of this criteria, you may find yourself sweating on your couch during the summer, freezing in your bed during the winter, and paying high energy bills year-round. Just take the time to educate yourself, and you could turn your house into the perfect oasis. Window technology has come a long way, but energy efficient windows require knowledge and precision.
According to the Consumer Guide to Home Energy Savings: Save Money, Save the Earth, “The best window glazing today insulate almost four times as well as the best commonly available windows from just fifteen years ago. Because of the rapid pace of change, even skilled designers are not fully aware of the potential these new glazings offer for energy efficient building design.”
Here are the Top 10 Criteria to Consider when Purchasing Energy Efficient Windows:
10. Reliability and Good Installation
It is important to make sure you have a good warranty because it is not uncommon for the air seal to fail causing fogging and low energy efficiency. Also, make sure you aren’t shooting yourself in the foot by hiring amateurs to install your windows.
9. Frame Material
The frame material is very important if you are looking to cut costs and save money. Wood is the most common material, and it is still considered to be an effective insulator. Vinyl is gaining in popularity, and in most cases, it is considered to be better than wood. Aluminum, however, is typically considered to be energy inefficient so avoid this option. There are a few other options, but these are the most common.
 (Vinyl Frame)
(Vinyl Frame)
8. Airtightness
Casement and awning windows are tighter than double-hung and other windows of the sliding variety. This is not always the case, but it is a good rule of thumb. Air leakage can be a huge issue so this is not something that you should overlook.
7. Multiple Layers of Glazing
Double glazed windows insulate twice as well as single glazed windows. There are also triple and quadruple glazed options. The extra layers will increase the effectiveness, but it may not necessarily be worth the extra cost if you live in a milder climate.
6. Thickness of Airspace
If your airspace between double-glazed panes is too thin (¼”), the insulation may not be sufficient. After about 1”, convection can occur and you could see a decrease in effectiveness. On a double glazed window, somewhere between a ½” and 1” is the sweet spot.
5. Low Conductivity Gas Fill
If you substitute are denser, lower conductivity gas like Argon between panes, you will see a huge leap in energy efficiency. If you are serious about saving money and the environment, look into these options.
4. Edge Spacers
Edge spacers are what hold the panes apart, and they can be an integral part of you saving money. Again, you are going to want to avoid aluminum when choosing your edge spacers. Instead, choose some that are thin-walled steel, silicon foam, or butyl rubber. If your window is fogging up, there is a chance that your edge spacers have failed. This is another reason to pay attention to the warranty.
3. Look for ENERGY STAR
Windows, doors, and skylights applying for the ENERGY STAR label must meet certain stringent requirements that vary by climate region. This is good to consider when you are looking to increase the energy efficiency of your home or business.
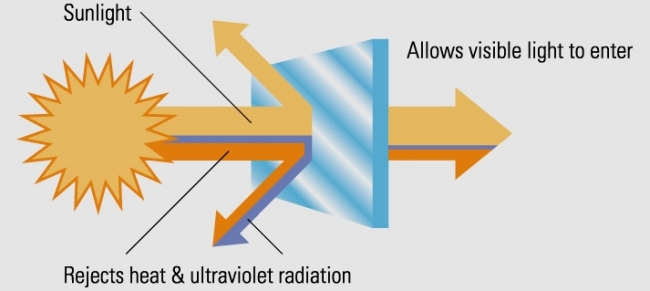
2. Glazing with Low Emissivity
According to Residential Windows: A Guide to New Techonologies and Energy Performance, there are two basic manufacturing processes for creating low emissivity (or low-E) glass, sputtered and pyrolytic. Low-E glazing has been called the greatest breakthrough in window technology in the last 30 years. Approximately 60% of windows sold in the US today have low-E coatings. It is an essential feature if you want to be energy efficient.
1. Window Properties and NFRC Ratings
In 1993, the NFRC created a standardized scale that can be used to measure and compare the performance of each window. The standardized scale measures five criteria:
- U-value: Measures the amount of heat moving through the window. The lower, the better.
- Solar Heat-Gain Coefficient: Measures how much solar heat is moving through the window. Above .6 or 60% is considered to be high. What you choose will depend on your climate region.
- Visible light transmittance: Measures how much light can make it through the window. Measure on a scale of 0 to 1 (with 1 being the highest.)
- Air leakage: Obviously measures the amount of air leakage. Sliding windows typically have the highest air leakage because that have to use seals that allows the window to slide.
- Condensation resistance: Measures the ability for the window to resist the formation of condensation on the inside surface of the window. The scale is between 0 and 100 (with 100 being the best.)
If you take the time to incorporate these criteria into your decision, you will enjoy the benefits for many years. Installing energy efficient windows is the smartest thing you can do for increasing the enjoyment of your home, increasing productivity in the workplace, reducing wasted energy, and increasing the sustainability of our world.
Brought to you by Glass Express, Inc.